Thickness is usually a dominant factor in choosing the perfect poly tarp as it affects durability, usability, and overall performance. Imagine needing to cover anything from equipment to outdoor furniture to construction materials; understanding the subtleties of tarp thickness will save you time, money, and frustration. This guide will help you decode the poly tarp thickness scenario to assist you in making decisions that cater to your needs. We’ll look into much lighter options fit for temporary use as well as heavy-duty ones that can take their beating through bad weather, together with the considerations so that you can entirely put into practice and determine the best tarp for your specific job.
Understanding Tarp Thickness
What is Mil Thickness?
Mil thickness is a U.S. standard unit used to specify material thickness, primarily in the industrial and commercial markets for tarps, plastics, coatings, etc. One mil equals one-thousandth of an inch (0.001 inch or 0.0254 mm). To provide some perspective, an average sheet of copy paper ranges from 3 to 4 mils in thickness.
Key Thickness Reference Points
- 1 mil = 0.001 inch (0.0254 mm)
- Copy paper = 3-4 mils
- Light-duty tarps = 5-8 mils
- Heavy-duty tarps = 20+ mils
For poly tarps, this thickness determines the sturdiness, flexibility, and application suitability. Thicker tarps, 20 mils or more, are considered heavy-duty and are, therefore, manufactured to sustain long periods of exposure in harsh environmental conditions-wind, rain, UV. Thin tarps of the order of 5 to 8 mils are light in weight and are best suited for temporary or less demanding assignments at a lesser price. Mil thickness is hence the deciding factor in choosing tarps that best fit your project, thereby ensuring maximum performance and life.
Factors Affecting Tarp Thickness
Several factors influence the correct choice of tarp thickness, closely linked to the final use and environmental conditions it may be exposed to. The primary consideration includes the requirement for strength and durability concerning capability. Under more than 16 mils thickness, tarps are a better choice for heavy-duty tasks, such as covering machinery and agricultural equipment, or for constructing temporary shelters where resistance to punctures or tearing is important. On the contrary, a thin tarp between 5 and 8 mils fits lightweight short-term projects, such as covering furniture during a paint job or keeping an item free from light debris or dust.
Environmental exposure also plays in favor of larger thick. For long exposure to UV radiation, high wind speed, or heavy precipitation, the thick tarp with a UV inhibitor and weatherproof coating is more suitable. The actual uses and frequency of use or wear themselves also determine thickness: for instance, thick tarps in the middle (10-15 mils) represent a compromise in functionality and workable endurance, whereas thinner tarps have more flexibility but tend to fade quickly. By looking at site search trends, it becomes evident that heavy-duty tarps are most commonly sought by consumers aiming at outdoor protection in extreme climates, which suggests that they associate such scenario with higher thick usage.
A careful consideration of these factors will help ensure users buy the correct tarp thickness for their specific project requirements, thus maximizing both cost-effectiveness and functional efficiency.
Common Thickness Levels for Tarps
In correlating common thickness levels for tarps to the latest trends from the search engine, the data shows clear preferences for specific thickness ranges depending on the application.
Analysis of these trends shows that user search behavior largely depends on contextual needs and environmental factors. This further stresses the importance of proper choice of tarp thickness based on the specific demands of a project.
Choosing the Right Tarp for Your Application

Light-Duty vs. Heavy-Duty Tarps
To decide on opting for a light- or heavy-duty tarp, it is best to consider the specific needs of the application, especially in light of recent data trends from search engines. Heavy-duty tarps are seeing increased demand in markets such as construction, agriculture, and disaster recovery, emphasizing a need for durability and weather resistance lasting long periods. On the other hand, light-duty tarps continue in favor for lighter and less-intensive operations, such as interim residential use-that is for covering furniture when working or two-hour outdoor protection.
Light-Duty Tarps (5-7 mils)
- Thinner polyethylene fabric
- Light-stress conditions
- Limited weather exposure
- Budget-friendly option
- Common searches: “light tarpaulins for garden use”
Heavy-Duty Tarps (10+ mils)
- Reinforced materials
- Severe weather conditions
- Extended UV exposure resistance
- Long-term durability
- Common searches: “strong tarpaulins for industrial use”
The foremost difference between light and heavy-duty tarps is the nature of material, thickness, and resistance to the elements. Search data reveals that consumers often query for “strong tarpaulins for industrial use” or “weatherproof tarpaulins for storms,” emphasizing the need for heavy-duty solutions in high-risk environments. Keywords such as “light tarpaulins for garden use,” meanwhile, represent uses where lightweight, less costly options are given priority. Corresponding these insights with the requirements of your project can aid in choosing a tarp type that guarantees performance and cost-effectiveness.
Choosing Tarp Size and Thickness
The size and thickness selection for a tarp need to be preceded by an assessment of the specific requirements of the intended application. The size of the tarp should be based on the actual dimensions of the area or object being covered. It is always useful to allow a margin to secure the tarp properly when the application is outdoors, or where movement could jeopardize the coverage, i.e., a little extra for the tarp to be tied down. Larger sizes may be suited for big jobs such as covering vehicle fleets or construction materials, while smaller tarps would suffice for home gardening tasks.
Thickness Selection Guidelines
- 5-7 mils: Lightweight, indoor applications or temporary outdoor use
- 8-10 mils: Medium-duty, moderate weather conditions – good weight/strength trade-off
- 12+ mils: Heavy-duty, industrial applications and harsh weather conditions
How thick the tarp should be will depend largely on things like the severity of exposure to the elements and length of battles with wear and tear. Recent search trends show increased interest in “thick tarps for outdoor protection,” emphasizing the need for durability when facing rough treatment. Selecting tarp size and thickness according to the use will maximize performance and value for cost.
Understanding Waterproof Capabilities
To answer how to gauge a tarp’s waterproof capabilities, one should look into the materials and coatings. High waterproof tarps would typically be those made of polyethylene or vinyl and with a laminate coating. These coatings, apart from repelling water, also repel molds and UV rays. Recent search trends show an increasing number in queries for the “best waterproof tarps for heavy rain,” or “tarps with UV protection”, indicating a much stronger customer preference for multi-functional solutions. Where applicable, consider this rating in millimeters of water column or hydrostatic head, giving you a quantified idea of the extent to which a tarp offers protection from water getting through. Integrating this data with individual requirements make for selecting a tarp that is highly dependable and durable.
Material Composition of Poly Tarps

Polyethylene Tarps Benefits
Polyethylene tarps are distinguished by high tensile strength, being lightweight, and their impressive resistance to the environment such as in terms of UV radiation, mold, and water. According to the latest search data (), it is very obvious that polyethylene tarps were considered as sought after for diverse uses, and the queries highlight uses in construction, agriculture, and recreational settings. Polyethylene tarps stand for exceptional wear longevity since their woven core design makes it harder for them to tear and get abraded during extended periods of use. Trying to maintain their chemical resistance against advanced modern applications would then lead to ownership under industrial environments because they would be charged with corrosive substances. The last attributes make it clear as to why polyethylene tarps are still getting ranked as a highly preferable solution for both industrial use and consumer-level general multi-purpose cover needs.
Durability Considerations
In determining the durability of polyethylene tarps, the interplay of material composition versus environmental stress factors must be looked at. By referencing the latest data on ‘s trends in search policies and related technical sources, common user queries related to these attributes focus on ultraviolet stability, tensile strength, and resistance to prolonged environmental exposure. Polyethylene tarps with UV inhibitors harnessed in their engineering should have heightened longevity because sunlight here refers to rays, ingested in degradation by ultraviolet rays. Tensile strength, on the other hand, is rated in pounds per square inch (PSI) and gives the indication of being able to withstand a certain weight and exertion on the tarp without tearing. For extreme environments, polyester tarpaulins with reinforced grid patterns or double stitching along the edges maintain performance against high winds, sharp objects, and variation in temperature. These features, together, make them reliable and useful in industrial, agricultural, and construction work, thus living up to their reputation for toughness and versatility.
Effect of Environmental Factors on the Performance of Tarps
UV Radiation Effects
Continuous exposure to UV rays renders polypropylene and polyethylene materials weaker in tensile strength and become brittle as time passes by.
Temperature Fluctuations
As temperature fluctuates, expansion and contraction cause weakness to the seams that could even bring out micro-tears.
Moisture and Precipitation
High temperature, and moisture, and precipitation promote mold and mildew, further deteriorating the rigidity.
Extremely environmental conditions strongly affect tarp performance and longevity, especially in outdoors. To get the best performance, prevent the tarp with a UV coating and keep a regular check on the wear so as to extend the life of these tarps even under severe environmental stress.
Tarp Usage Scenarios
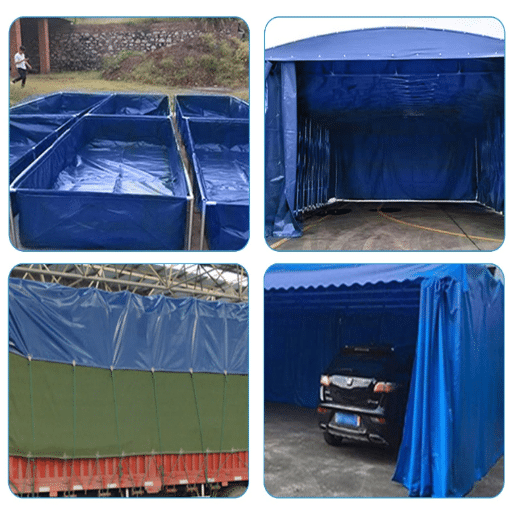

Small Tarps Conducted in Everyday Use
Small tarps offer a range of practical applications in daily life. For example, they are often used in protecting outdoor furniture from UV radiation, rainwater, and debris. Gardeners utilize small tarps to collect leaves, soil, or other materials to cut down on clean-up time and mess. Small tarps are also employed by contractors and DIY-ers during painting or renovation to prevent paint-splatter or dust from settling on floorboards and furniture.
Popular Small Tarp Applications
- Outdoor furniture protection
- Garden debris collection
- Paint job floor protection
- Camping temporary canopy
- Emergency weather shelter
The latest search trends analyzed show that in recreational activities such as camping and picnicking, small tarps frequently find their application as a temporary canopy or shelter. Being lightweight and quick to set up, they provide vital relief from an unpredicted weather change. This adaptability and cheapness for small tarps have positioned them as an indispensability in professional work and everyday convenience.
Heavy Duties for Industrial Uses
Due to their excellent sturdiness and versatility, heavy-duty tarps have gained industrial sectors’ respect. Common inquiries from users based on recent data retrieved from ‘s search engine focus on construction, agriculture, and transportation as primary areas for tarp use. These are generally placed over machinery, scaffolding, and building materials to keep harsh weather conditions and contaminants at bay.
Construction
Machinery, scaffolding, building materials protection
Agriculture
Ground covers, silage covers, equipment protection
Transportation
Cargo protection, safety compliance
These also find application in agriculture as ground covers, silage covers, or as weather barriers for equipment and crops. Their longevity and resistance to tearing make an excellent cost-effective option for any business that will be regularly subjecting them to hard usage. Heavy-duty tarps are used to tie down and protect cargo during long-distance transit in adherence to safety and compliance standards. This reflects increasing dependence on tarps as an essential tool to aid industrial operations.
Best Practices in Tarp Maintenance
Maintenance should be undertaken if one wants to extend the operational life of heavy-duty tarps, especially under heavy industrial or agricultural usage. Regular inspection should be undertaken to spot early signs of wear such as small tears, frayed edges, or weakened grommets. It is best to wash your tarp using mild detergents with a sponge and water to remove dirt or debris and possible chemicals that could eventually eat off the tarp surface layer. Avoid using abrasive cleaning pads and harsh chemicals because they will gradually destroy the tarp’s outer coating.
Maintenance Best Practices
- Regular inspection for tears, frayed edges, or weakened grommets
- Clean with mild detergents and soft sponge
- Avoid abrasive cleaning pads and harsh chemicals
- Store in cool, dry location away from direct sunlight
- Fold or roll neatly to avoid creases
- Apply UV protection treatments when needed
When not in use, tarps should be stored in a cool, dry location away from direct sunlight to avoid UV degradation, with this considered one of the main reasons for material weakening. In addition, folding or rolling tarps neatly instead of crumpling them will help avoid the formation of creases that may later contribute to structural weakness. UV protection treatments or sprays could further enhance the life of tarps in the field.
Search query statistics by ‘reflect: “how to maintain tarps” point towards increasing concern about UV-protection and water resistance. The study places value on buying materials that incorporate additional UV resistance and appropriate waterproofing even during the purchasing stage. By doing so, organizations or individuals extend the usefulness of their overall stock through alternative means such as rotating several tarps to reduce stress and wear on one particular unit.
Frequently Asked Questions
How does one choose the perfect tarp thickness?
Choosing the right tarp thickness depends on the intended application of the tarp. Thicker tarp materials, usually measured in mils, say 20 mils, are good for heavy applications like construction sites or in covering outdoor equipment during harsh weather. For lighter duties such as covering firewood or providing shade for a short time, one would go for thinner tarps in the range of 5 to 6 mils. Durability and longevity should always be considered when selecting tarps; a thicker tarp could better resist tearing and puncturing. Also, if you are intending to use your tarp in an area exposed to UV radiation, it would be wise to ensure it has been manufactured using a UV-resistant material.
Why should I use a poly tarp?
Poly tarps are famous because they are versatile and durable. These tarps will generally be waterproof and will stand up to tough conditions, so they could be used for covering equipment or setting up temporary shelters. But in comparison to heavier canvas tarps, poly tarps do weigh much less, which is an important point for those who intend for fast installations. Furthermore, poly tarps are often treated to be tear-resistant, enhancing their longevity under different conditions. When shopping for a poly tarp, make sure that it has reinforced edges and rust-resistant grommets for added durability and protection over time.
What size tarp should I use for my project?
Selecting that tarp size is very important for proper coverage. Thus take measurements of whatever you plan to protect and add extra length in case heavy rains or strong weather conditions can come on during the project. Different sizes are available for tarps, so you can find what you need for a small tarp for light-duty work or the super heavy-duty tarp for big coverage. It is important that, apart from fitting the dimensions of your project, it is also thick enough for its intended use; while at it, always check the tarp specification and see if it mentions anything about average thickness in mils.
Heavy duty versus lightweight?
Heavy duty tarps, being thicker usually in the 10 to 20 mil range, provide the most protection from tears and punctures and are therefore used for demanding applications such as construction sites or long-term outdoor use, in adverse weather conditions. On the other hand, lightweight tarps of around 5 to 6 mils being suitable for light-duty applications such as temporary shade, or covering things that do not require heavy protection. They are somewhat easier to drag around than heavy-duty tarps but cannot match them for durability or longevity. Basically, the decision between heavy duty and lightweight tarps comes down to the needs of the project at hand.
Are mil thickness ratings important for tarps?
Yes, mil thickness ratings matter when your decision is based on tarps; they denote the durability and strength of the material. A mil is one-thousandth of an inch, and the thickness of a tarp gives an edge in resisting harsher weather conditions, with those thicker ones rated 20 mils seldom to tear or puncture. For example, a poly tarp for heavy-duty application will be somewhere in the thickness range of 10 to 20 mils, to give protection to equipment or provide shelter. Thinner tarps, say around 5 to 6 mils, are used for lighter chores. Understanding mil thickness ratings help one to choose the appropriate tarp for their specific needs, thus ensuring maximum protection.
Reference Sources
- Academia.edu – Design of the Tool for Pressing of Tarpaulin Grommets: This paper discusses the design and strength of tarpaulins, including considerations for thickness and durability. Link to source
- Oregon State University – Weather Ballooning Program: This research mentions the use of tarps with varying thicknesses for specific applications, such as weather balloon setups. Link to source
- UMass ScholarWorks – Pesticide Mixing and Loading: This document highlights the importance of tarp thickness for containment surfaces in agricultural applications. Link to source



